Social touch promotes communication via oxytocin
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Have you ever experienced a warm embrace that made you feel loved and cared for? Or perhaps a friendly pat on the back that lifted your spirits? These moments of gentle touch not only provide comfort but also release a powerful hormone called Oxytocin, which has been found to have numerous benefits for our mental and emotional health.
Oxytocin and the Power of Non-Sexual Touch in Relationships
Many people associate Oxytocin with sexual intimacy, but it is much more than that. Oxytocin is a hormone that is naturally produced in our bodies, and its release is linked to physical touch. While sexual intimacy can trigger the release of Oxytocin, non-sexual touch, such as hugging, holding hands, or a friendly touch, can also boost the hormone’s levels in our body.
Oxytocin has been linked to a variety of positive effects, including reduced stress levels, lower blood pressure, and increased feelings of trust and bonding. This hormone plays a crucial role in our relationships and can help cement our connections with others.
The Target of Oxytocin and the Power of Non-Sexual Touch in Relationships
When we experience physical touch, our brain releases Oxytocin. This hormone acts as a neurotransmitter, which allows signals to be transmitted from one nerve cell to another. Oxytocin affects our social behavior by increasing our empathy and trust towards others while reducing anxiety and fear.
A personal experience that highlights the power of non-sexual touch in relationships is feeling soothed and cared for when someone gives a hug or a reassuring touch on the hand during difficult times. Oxytocin helps us bond with others, making those moments of touch even more meaningful and powerful.
The Benefits of Oxytocin
In addition to its role in social bonding, Oxytocin has also been found to have several other benefits. Studies have shown that Oxytocin can reduce inflammation in the body and promote wound healing. It can also enhance feelings of happiness and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Oxytocin can even reduce cravings for addictive substances like alcohol and drugs by regulating our reward center in the brain. This hormone’s ability to reduce stress levels and increase feelings of trust and empathy can also have indirect but positive effects on our overall health and well-being.
How to Increase Oxytocin Levels
While sexual intimacy is one way to boost Oxytocin levels, it’s worth noting that non-sexual touch can also have a significant effect. Simple gestures like holding hands, hugging, or gentle touches can all increase this hormone’s levels in our bodies. Spending time with loved ones and engaging in social activities can also promote Oxytocin release.
The Power of Non-Sexual Touch
The power of non-sexual touch in relationships cannot be overstated. It can be a simple yet powerful way to connect with others, both physically and emotionally. Whether it’s a pat on the back, a hand squeeze, or a warm embrace, these small acts of touch can release Oxytocin, which can promote feelings of empathy, trust, and connection. So the next time you’re feeling stressed or anxious, reach out and give someone a hug. You might be surprised by how much better you feel.
Question and Answer
Q: Can Oxytocin be produced without physical touch?
A: Yes, Oxytocin can be produced in our bodies without physical touch. For example, positive interactions like laughing, singing, or even watching a heartwarming movie can trigger the release of Oxytocin.
Q: Does Oxytocin have any negative effects?
A: While Oxytocin is generally considered safe and beneficial, excessive levels of the hormone can lead to unwanted side effects like nausea, headaches, and changes in appetite. It’s always best to talk to a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your Oxytocin levels.
Q: Can Oxytocin increase our pain tolerance?
A: Yes, Oxytocin has been found to have pain-relieving effects. This hormone can reduce pain sensitivity and increase pain tolerance, making it a valuable tool in managing chronic pain conditions.
Q: How does Oxytocin affect our social behavior?
A: Oxytocin plays a crucial role in our social behavior by increasing our empathy and trust towards others while reducing anxiety and fear. This hormone can promote feelings of bonding and connection, making it an essential component of our relationships.
Conclusion of Oxytocin and the Power of Non-Sexual Touch in Relationships
Oxytocin is a hormone with significant effects on our mental and emotional well-being. Its release is triggered by physical touch, including non-sexual touch, and has numerous benefits for our health. By engaging in moments of gentle touch, we can tap into the power of Oxytocin and experience feelings of trust, empathy, and connection with others. So the next time you’re feeling stressed or anxious, reach out and give someone a hug. Your body and mind will thank you for it.
Gallery
The Healing Power Of Soothing Touch - Mindful Methods For Life
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin healing touch power soothing
» Human Touch And Our Internal Connection To Beauty Beauty Blog
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin hormone hug gland brain released porn ted stress pituitary beauty releases when forth author young gary wilson effects talk
Deric’s MindBlog: How Oxytocin Enhances Male Sexual Activity
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin
Bring Intimacy Pleasure And Desire Back Into Your Life
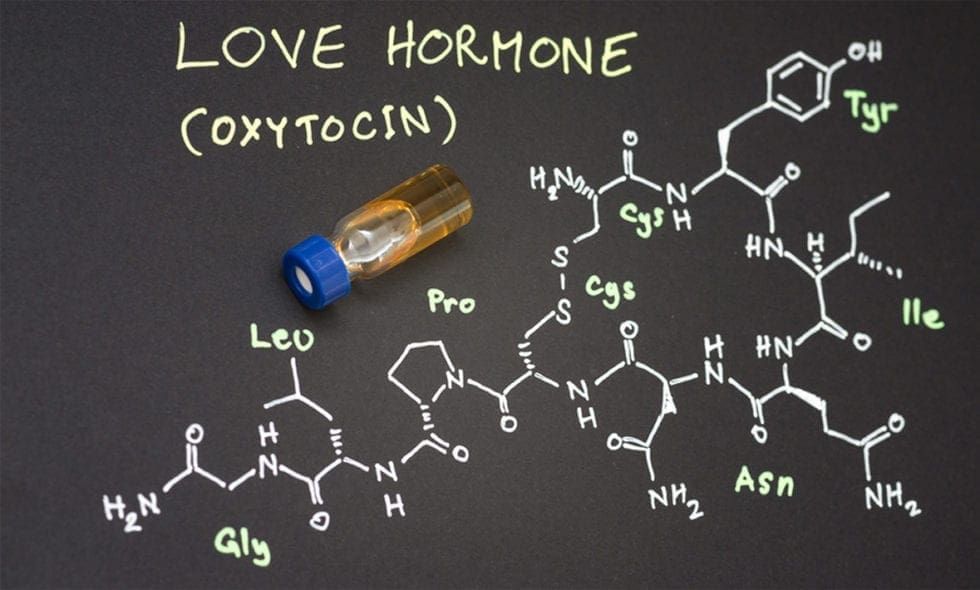
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin
Social Touch Promotes Communication Via Oxytocin | Human Frontier
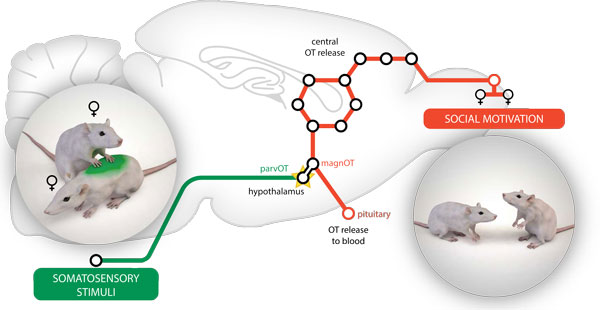
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin promotes