Oxytocin role hormone pituitary pregnancy secreted effects posterior gland released diabetes cells secretion when hormon hypothalamus metabolic dual osteoporosis two
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
The Power of Touch: How Oxytocin Enhances Relationship Trust
Have you ever felt a sense of connection and trust after a warm embrace or tender touch? This feeling can be attributed to the hormone oxytocin, also known as the “love hormone”. Oxytocin plays a vital role in enhancing relationship trust and bonding.
Many people struggle with trust issues in their relationships. These issues can lead to feelings of insecurity, anxiety, and even depression. Oxytocin can help alleviate these pain points and promote positive emotions in relationships.
So, what exactly is the target of oxytocin in enhancing relationship trust? Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus, a region in the brain responsible for regulating social behaviors. When we engage in positive social interactions, such as touch, our brain releases oxytocin, promoting feelings of trust and closeness.
Research shows that oxytocin can strengthen the bond between partners, increase feelings of affection and empathy, and decrease stress levels. By promoting positive social interactions, oxytocin can play a significant role in enhancing relationship trust and intimacy.
The Power of a Hug
When I think about the power of touch, I think of a moment when I hugged my partner after a long day at work. The embrace felt like a sigh of relief, and I felt a sense of calm wash over me. This moment was a result of oxytocin being released in my brain.
When we engage in physical touch, such as a hug, handshake, or even a pat on the back, our brain releases oxytocin. This hormone promotes feelings of trust and bonding between individuals. By engaging in positive physical touch, partners can strengthen their emotional connection and enhance trust in their relationship.
Non-Physical Touch
Physical touch isn’t the only way to release oxytocin and enhance relationship trust. Activities such as spending quality time together, engaging in acts of kindness, and expressing love and gratitude can all promote the release of oxytocin in the brain. Non-physical touch is just as important in promoting relationship trust and bonding.
The Importance of Oxytocin in Long-Distance Relationships
Long-distance relationships can be challenging, but oxytocin can still play a role in promoting trust and intimacy. Simple acts such as sending a care package or writing a love letter can promote the release of oxytocin and strengthen the bond between partners. By engaging in positive social interactions, even from afar, couples can enhance their trust and deepen their emotional connection.
The Role of Touch in Rebuilding Trust
Trust can be challenging to rebuild after a breach. However, touch can play a vital role in promoting healing and reestablishing trust. Positive physical touch, such as a hug or holding hands, can promote feelings of closeness and connection. By engaging in positive social interactions and touch, partners can enhance their emotional connection and rebuild trust in their relationship.
Question and Answer
Q: Can oxytocin enhance trust in all types of relationships?
A: Yes, oxytocin can promote trust and bonding in all types of relationships, including romantic relationships, friendships, and even between strangers.
Q: Can a lack of physical touch lead to a lack of trust in a relationship?
A: Yes, physical touch is a vital aspect of promoting oxytocin release and enhancing relationship trust. A lack of physical touch can result in feelings of disconnection and insecurity in a relationship.
Q: How can oxytocin help with anxiety and depression?
A: Oxytocin promotes feelings of relaxation and calmness, which can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Q: Can non-physical touch enhance oxytocin release?
A: Yes, engaging in positive social interactions, such as spending quality time together or expressing love and gratitude, can promote the release of oxytocin.
Conclusion of Oxytocin and the Role of Touch in Enhancing Relationship Trust
Oxytocin plays a powerful role in enhancing relationship trust and bonding. By engaging in positive social interactions and physical touch, individuals can promote the release of oxytocin and deepen their emotional connection with their partners. Oxytocin is not only essential in promoting trust and intimacy in romantic relationships, but also in all types of relationships. So, go ahead and embrace the power of touch in enhancing your relationship trust.
Gallery
What Is The Role Of Oxytocin In Men? | Betterhelp
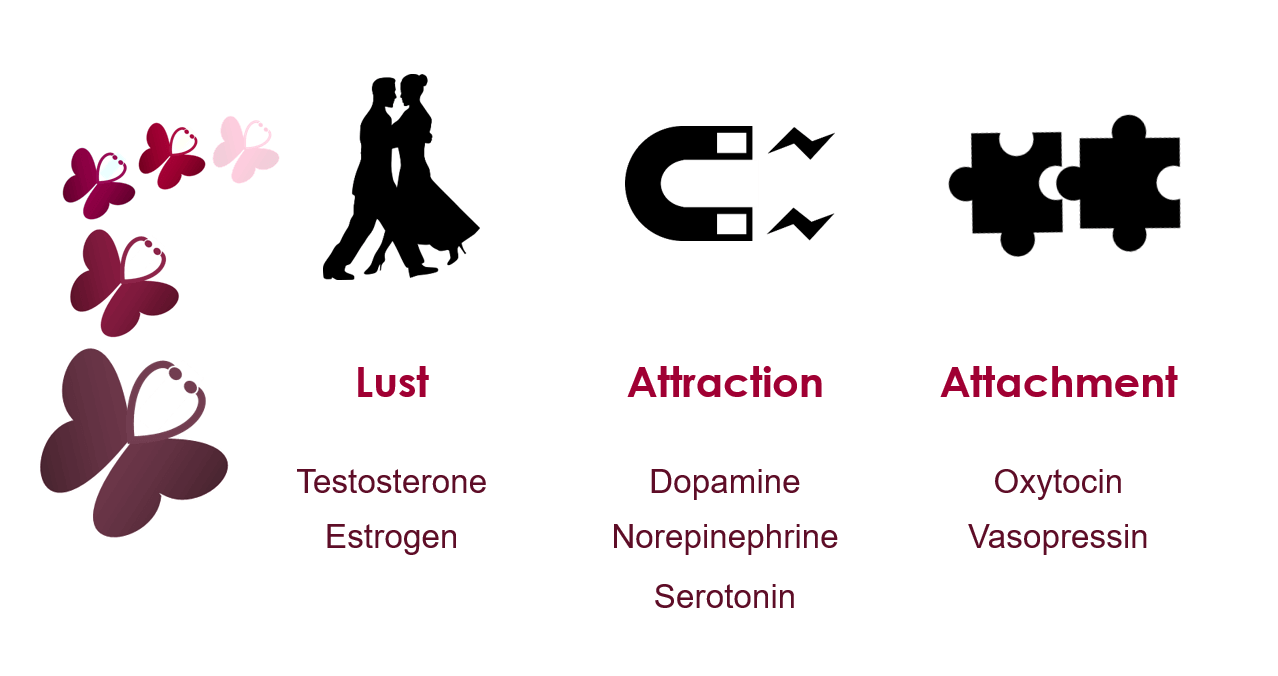
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin lust attraction role vs men hormones hormone science dopamine attachment companionship behind three relationship fall why serotonin when vasopressin
Frontiers | Two Birds With One Stone: Possible Dual-Role Of Oxytocin In
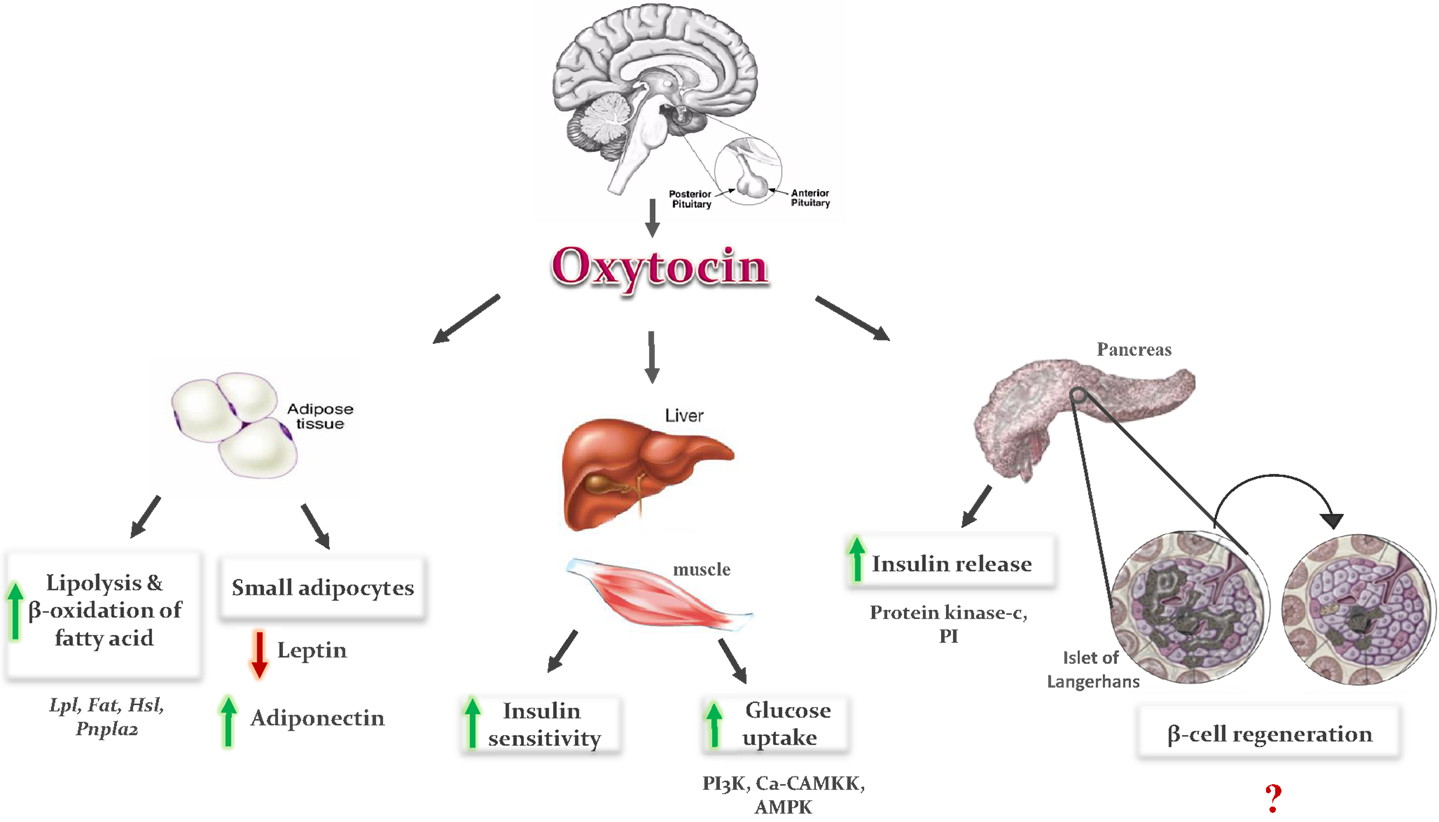
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin role hormone pituitary pregnancy secreted effects posterior gland released diabetes cells secretion when hormon hypothalamus metabolic dual osteoporosis two
Oxytocin: The Love Hormone | Why We Need It | How We Can Get It
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin hormone neurotransmitter
» Human Touch And Our Internal Connection To Beauty Beauty Blog
Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin hormone hug gland brain released porn ted stress pituitary beauty releases when forth author young gary wilson effects talk
Oxytocin Affects Response To Social Touch

Photo Credit by: bing.com / oxytocin touch response social increases difficulty patients serious ban put many would perception increased pleasantness subjects administration recent study female



